Estimating Hydrant Discharge Using Flow Emitters
Another way to model the discharge from a hydrant is to use flow emitters. A flow emitter relates the discharge to pressure immediately upstream of the emitter using:
The pressure exponent, n, is a variable that can be set in the Hydraulic Analysis Options section of the Calculation Options dialog box. The default value is 0.5, which should be used when using flow emitters to model hydrant outlets.
You should be able to model a hydrant as a flow emitter and enter the appropriate value for K. Not all of the energy available immediately upstream of the hydrant is lost, however. Instead, some of the energy is converted into increased velocity head, especially for the smaller (2.5 in, 63 mm) hydrant outlet.
In order to accurately model a hydrant, the model must be given an overall K value, which includes head loss through a hydrant and conversion of pressure head to velocity head. AWWA Standards C502 and C503 govern the allowable pressure drop through a hydrant. For example, the standards state that the 2.5 in. outlet must have a pressure drop less than 2.0 psi (1.46 m) when passing 500 gpm (31.5 l/s).
The energy equation can be written between a pressure gauge immediately upstream of the hydrant and the hydrant outlet:
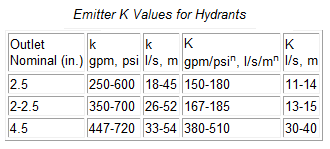
The difference between K and k is that K includes the terms for conversion of velocity head to pressure head. k is known, but K is the value needed for modeling.
A typical hydrant lateral in North America is 6 in. (150 mm) and typical outlet sizes are 2.5 in. (63 mm) and 4.5 in. (115 mm). Values for k vary from minimum values, which can be back calculated from AWWA standards, to much higher values actually delivered by hydrants. Values for K for a range of k values for 6 in. (150 mm) pipes are given below.
The coefficients given are based on a 5 ft. (1.5 m) burial depth and a 5.5 in. (140 mm) hydrant barrel. A range of values is given because each manufacturer has a different configuration for hydrant barrels and valving. The lowest value is the minimum AWWA standard.